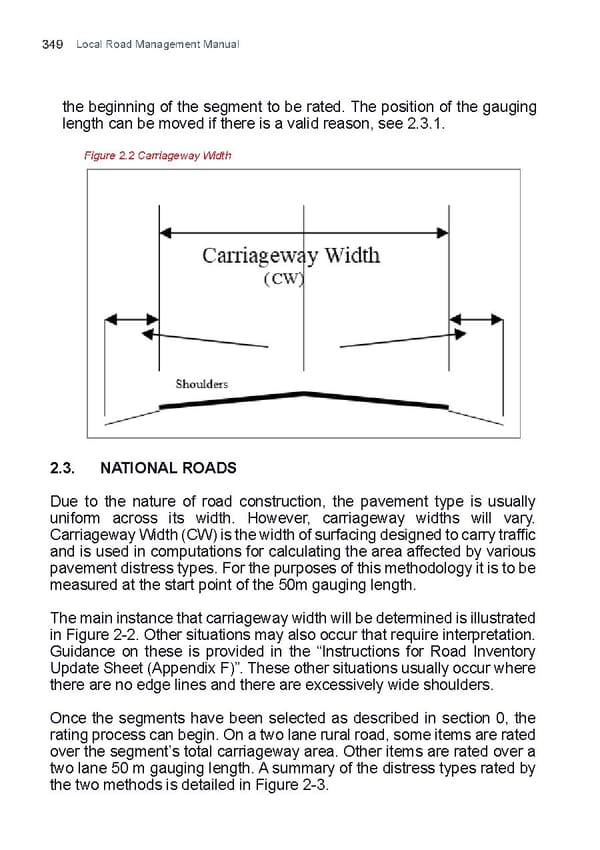
Local Road Management Manual 349 the beginning of the segment to be rated. The position of the gauging length can be moved if there is a valid reason, see 2.3.1. Figure 2.2 Carriageway Width 2.3. NATIONAL ROADS Due to the nature of road construction, the pavement type is usually uniform across its width. However, carriageway widths will vary. Carriageway Width (CW) is the width of surfacing designed to carry traiffc and is used in computations for calculating the area affected by various pavement distress types. For the purposes of this methodology it is to be measured at the start point of the 50m gauging length. The main instance that carriageway width will be determined is illustrated in Figure 2-2. Other situations may also occur that require interpretation. Guidance on these is provided in the “Instructions for Road Inventory Update Sheet (Appendix F)”. These other situations usually occur where there are no edge lines and there are excessively wide shoulders. Once the segments have been selected as described in section 0, the rating process can begin. On a two lane rural road, some items are rated over the segment’s total carriageway area. Other items are rated over a two lane 50 m gauging length. A summary of the distress types rated by the two methods is detailed in Figure 2-3.
 LRM Manual CMGP Page 348 Page 350
LRM Manual CMGP Page 348 Page 350